- Kenya is considered a poor country with a vast majority of the populace being peasant farmers in the rural areas.
- The gap between the few filthy rich individuals and the majority poor has continued to widen over the years.
- Poor governance, corruption and bad government policies are the main reason the Kenyan people continue to remain poor.
- The country has a development blueprint dubbed Vision 2030 that aims at uplifting millions of its people from poverty to middle income status by 2030.
Kenya has been ranked the top East African economic powerhouse for many decades.
The reason for its economic growth is mainly attributed to political stability and the strong growth of sectors like service industry, financial sector and agriculture.
The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and Per Capita income of Kenya has been on a steady rise for many years with strong bounce-backs from recessions such as the one induced by the Covid-19 pandemic.
However, the rosy GDP and Per Capita income figures are nothing close to the reality on the ground.
Most of the wealth in Kenya is concentrated in the hand of a small portion of the population and the inequality gap between the rich and the poor continues to widen year in year out.
It is a country of ironies and contrasts as many Kenyans wallow in abject poverty as most of them are peasant farmers and pastoralists with low living standards.
Main Factors Contributing to Poverty in Kenya
Poverty among Kenyans is caused by a myriad of factors. Here are the main reasons the Kenyan people will continue to be poor:
I. Marginalization
Bad governance in public and private sectors has led to skewed allocation of resources which results in marginalization that locks out millions of Kenyans from accessing basic amenities and services like education, access to clean water and health.
For many years, government-sponsored development projects have only been concentrated in a few regions with nothing much to show in the rest of the country.
The most affected regions by government marginalization are mainly the arid and semi-arid (ASALs) regions.
The ASALs in Kenya have the highest poverty index.
Upon the promulgation of the new constitution of Kenya in 2010, an equalization fund was established to help prop up development like water provision, healthcare and electricity projects in historically marginalized areas.
However, ten years since its implementation, the fund has not achieved much due to low disbursement of funds, legislative hurdles and political interference.
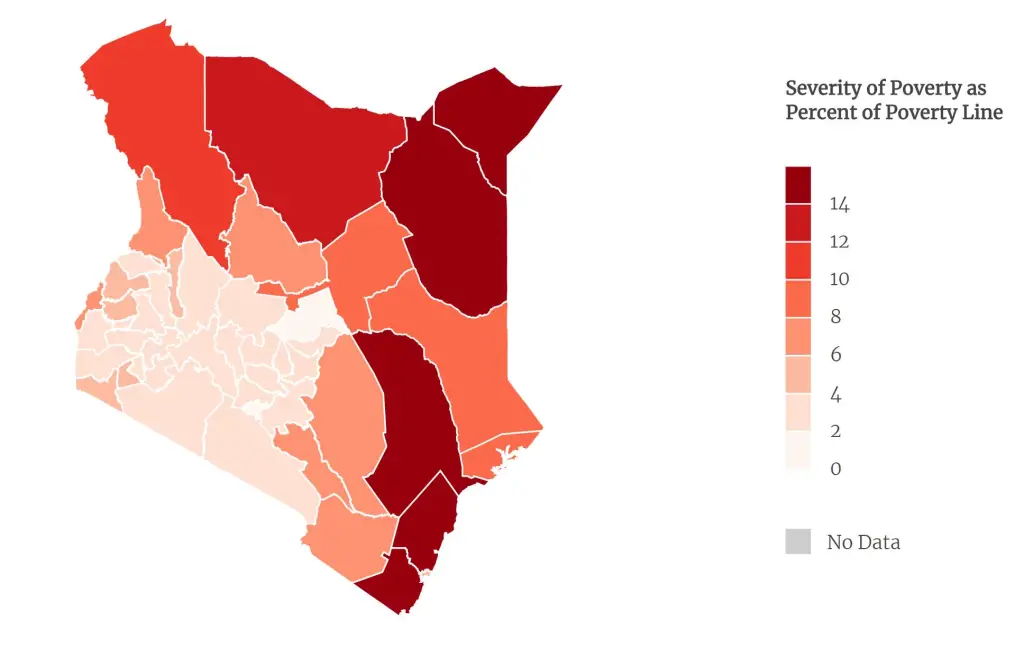
Map of Kenya showing poverty severity across the counties. ASAL counties are the poorest in Kenya due to decades-long marginalization.
Source: Society for International Development (SID)
II. Illiteracy and Ignorance
Kenya has made tremendous improvement in the education of its people.
However, there are still some sections of the population, especially in rural Kenya, that remain illiterate to-date.
The high illiteracy levels of yester-years caused massive poverty and ignorance whose effects have been an uphill task to reverse.
Illiteracy and the associated ignorance are known to cause poverty by curtailing an individual’s ability to secure meaningful jobs consequently leading to lower standards of living.
Less educated people also tend to be less exposed thus their thinking capacity is limited and so are their problem solving skills.
A special type of illiteracy that keeps the masses in Kenya poor is financial illiteracy.
A report by the Global Financial Literacy Survey shows that only 38% of adult Kenyans are financially literate.
Even well-educated Kenyans with decent jobs are just a payslip away from poverty because of poor personal financial management skills.
Most Kenyans struggle to maintain a healthy savings culture and in identification of investment opportunities.
Financial illiteracy also leads to reduced access and proper management of credit.
These challenges make it difficult for a majority of Kenyans to create generational wealth pull themselves out of poverty.
III. Unemployment
Another major cause of poverty in Kenya is the high unemployment rate.
Despite the population being highly educated and skilled, the Kenyan economy lacks the capacity to effectively absorb all working age Kenyans.
The number of jobless Kenyans has risen in recent years as the cost of living continued to soar.
This has led to many university and college graduates to take up menial jobs to survive as they endlessly search for meaningful job opportunities.
Unemployment also causes high dependency ratio and black tax in Kenya thus, trapping millions in a vicious cycle of poverty.
Breaking the poverty cycle becomes literally impossible because the meager earnings many Kenyans get are not enough to cater for all dependents, pay bills and leave some savings for investment.
According to Statista.com, the rate of unemployment in Kenya dropped steadily from 3.13% in 1999 to 2.76% in 2016, before rising sharply to 5.5% between 2017 and 2022.
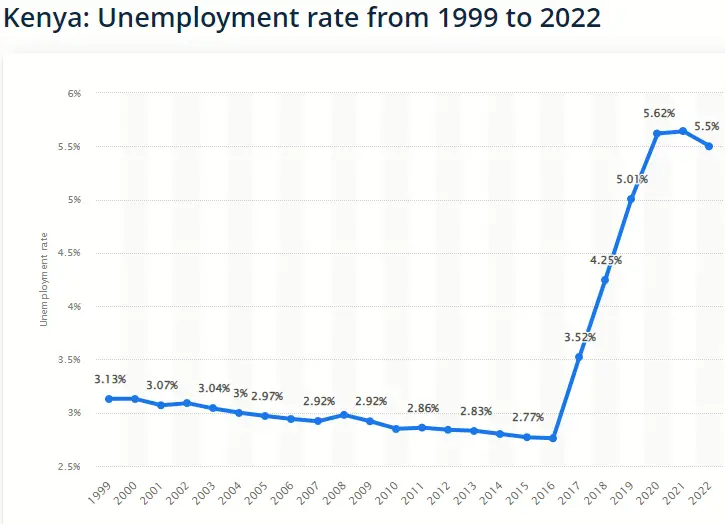
Source: Statista 2023
Can Kenya Achieve a Rich Country Status?
Although Kenya is a developing country that has already achieved a lower middle income status, the country still has a long way to go if it were to achieve a high income or first world status.
The country has in place a medium term development blueprint dubbed Vision 2030 that seeks to elevate the economy to a middle income status by 2030.
The achievement of vision 2030 is seen as a milestone that will act as a stepping stone to propel the country to rich country status.
Despite the goals and vision being set, Kenya’s achievement of rich country status is a far-fetched dream as the country faces inadequate financing of key projects, poor governance, corruption and retrogressive politics among other setbacks.
The country is likely to not achieve the much coveted rich country status unless serious reforms are undertaken to tackle the setbacks.
What Efforts is the Government Putting Forth to Reduce Poverty in Kenya?
Besides the Vision 2030 and the equalization fund, there are other Kenyan government initiatives such as the National Constituency Development Fund (NCDF) and the National Government Affirmative Action Fund (NGAAF).
These funds are aimed at funding socio-economic development programmes in the constituencies and counties.
The government has also sought partnership with Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) and other governments to work on poverty eradication programs across the country.
Through such partnerships, various projects including provision of clean water, building of schools and hospitals, agricultural projects among others have been accomplished.
What are Some Potential Solutions or Strategies to Address Poverty in Kenya?
Strategies like the Vision 2030, Bi-lateral and NGO partnerships have the potential to turn around the fortunes of the poor millions of Kenyas.
The government also needs to stamp out corruption and create well thought out strategic policies to spur the economy and eradicate poverty among the masses.
Policies that eliminate marginalization of some regions in the country should be fully implemented to boost uniform distribution of resources and nationwide prosperity.
Priority should be given to the most pressing needs of the Kenyan people like food security, access to clean water, access to affordable healthcare, education and job opportunities.
These form the basis for a massive take-off to prosperity of the people of Kenya.
Parting Thoughts
In sum, Kenya is still a poor country despite the massive potential it has to become the most prosperous and economically advanced country in Africa.
The poverty rates have not improved much in the sixty years since the country gained independence.
This fact raises questions on the Kenyan government’s commitment to weed out poverty yet Kenyans are always working hard to pull themselves out of the quagmire.
The skewed distribution of the national cake and infiltration of major economic sectors by cartels has locked so many Kenyans out of life-changing opportunities.
The Kenyan people can only achieve collective prosperity if they put aside negative ethnicity, nepotism, corruption and retrogressive politics and hold their national leaders accountable for their actions or lack thereof.
As much as there is hope for a better Kenya in future, a lot needs to be done if the country’s full potential is to be realized and elevate the country to the much hyped league of rich countries.
You may also want to check:

