Kenya, a vibrant East African nation, follows a democratic republic system of governance, emphasizing the power of the people in shaping their government.
With a multi-party democracy, the country embraces a balanced separation of powers among its executive, legislative, and judicial branches.
In this post, I will dig deep into the structure and functions of Kenya’s government system, highlighting the key features and providing an insightful overview.
A Democratic Republic
Kenya operates under a democratic republic framework, where the head of state is an elected president rather than a monarch.
This political arrangement allows citizens to participate in the decision-making process through periodic elections.
Multi-Party Democracy
Kenya’s political landscape thrives on a multi-party system, ensuring diverse political ideologies and representation.
Multiple political parties actively compete for power in elections, providing voters with various choices and fostering a healthy democratic environment.
Through the multi-party democracy, Kenya offers a platform for robust political debates, policy discussions, and peaceful power transfer.
Citizens can engage in active political participation, making their voices heard through voting and supporting the parties and candidates that align with their vision for the country’s future.
The multi-party system in Kenya also encourages accountability and transparency.
Political parties play a crucial role in scrutinizing the government’s actions, challenging policies, and advocating for the interests of their constituents.
This system creates a checks-and-balances mechanism, ensuring that no single party or group can dominate the decision-making process without scrutiny.
Separation of Powers: The Three Branches of Government
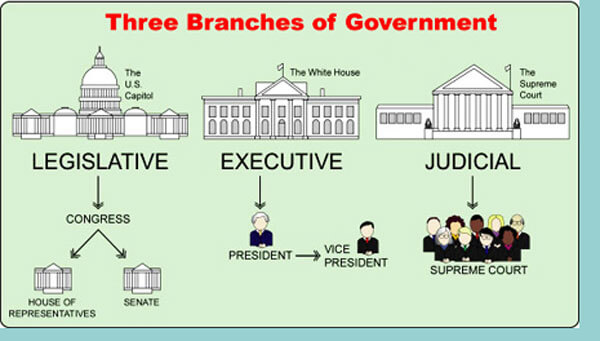
A fundamental aspect of Kenya’s government system is the separation of powers, which ensures a balance of authority and prevents the concentration of power in a single entity.
The government is divided into three branches: the executive, legislative, and judicial, each with distinct roles and responsibilities.
I. The Executive Branch (Major Role: Implementing Laws and Leading the Nation)
At the helm of the executive branch is the president, who serves as both the head of state and the commander-in-chief of the armed forces.
The president, elected by popular vote for a five-year term, is responsible for implementing and executing the country’s laws.
They also appoint the cabinet, composed of ministers responsible for overseeing various government departments and ensuring the smooth functioning of the administration.
II. The Legislative Branch (Major Role: Crafting and Enacting Laws)
The legislative branch comprises the National Assembly and the Senate.
The National Assembly, with 349 members elected through popular vote, represents constituencies across the nation.
The Senate, consisting of 67 members, is elected by the counties.
Together, these bodies hold the power to make and pass laws that govern the country.
They engage in debates, discussions, and legislative processes to ensure that the laws enacted align with the needs and aspirations of the people.
III. The Judicial Branch (Major Role: Safeguarding the Rule of Law)
Kenya’s judicial branch, headed by the Chief Justice, plays a crucial role in interpreting and applying the country’s laws.
The president appoints the Chief Justice with the National Assembly’s approval.
The judiciary ensures the impartial interpretation and enforcement of laws, safeguarding the rights and liberties of the citizens.
The Supreme Court, as the highest court in Kenya, acts as the final authority in legal matters, providing a mechanism for resolving disputes and upholding the principles of justice and fairness.
Separating powers ensures a system of checks and balances, preventing any branch from abusing its authority.
This balance fosters accountability, transparency, and democratic governance by ensuring that no single entity holds absolute power.
It allows for effective oversight, cooperation, and collaboration among the branches, contributing to the stability and progress of the nation.
Unitary State Structure

Kenya’s government system operates under a unitary state structure, where power and authority are primarily concentrated at the national level.
This structure allows for a cohesive and centralized governance framework while recognizing the need for local representation and administration through counties.
Centralized Governance
In a unitary state, the central government holds significant decision-making powers and exercises authority over various aspects of governance, including national defense, foreign policy, and economic planning.
The central government is responsible for formulating and implementing policies that impact the entire nation, ensuring uniformity and consistency in governance across different regions.
Devolution of Power: Counties and Local Autonomy
Recognizing the importance of local representation and addressing regional needs, Kenya adopted a devolved system of governance in 2010.
The country is divided into 47 counties, each with its own elected government.
This devolution process aimed to empower local communities and promote inclusive governance.
County governments oversee healthcare, education, infrastructure development, agriculture, and public service delivery within their jurisdictions.
This decentralization of power allows for more focused attention on individual regions’ specific needs and priorities, ensuring better responsiveness to local challenges and opportunities.
While the central government sets national policies and standards, counties have the authority to implement these policies at the local level.
This arrangement enables counties to tailor their development plans and strategies to address their communities’ unique socio-economic and cultural dynamics.
Additionally, counties have the power to generate revenue through local taxation and other sources, providing them with financial autonomy to fund local initiatives and projects.
Final Verdict
Ultimately, Kenya’s government system, characterized by a democratic republic and a unitary state structure, reflects the country’s commitment to inclusive governance, citizen participation, and effective decision-making.
With a multi-party democracy, Kenya provides diverse political representation, while the separation of powers ensures accountability and prevents the concentration of authority.
Additionally, the devolved system of governance empowers counties to address local needs and foster regional development.
Together, these elements create a balanced and dynamic government system that serves the aspirations and interests of the Kenyan people.
You may also want to check:

