The history of Kenya is a rich and diverse one, with many different peoples having contributed to the country’s cultural heritage.
There are four main language groups in the country namely; Nilotes, Cushites, Bantus, and Semites.
Granted, the Semites are rarely thought of as a Kenyan language group but as we will see shortly, it is an important group to the social and cultural fabric of the country.
What are Semites?

The term “Semite” refers to a group of people who share a common language family, known as the Semitic languages.
This group includes people from the Middle East and North Africa, such as Arabs, Jews, and Ethiopians, among others.
Semite, in reference to race, was coined in the 1770s at the Gottingen School of History and has since been used although it may not be as common today because some consider the term a racial slur.
Examples of Semites in Kenya
Several language groups are classified as Semites but the most popular Semitic group in Kenya is the Arabs.
The Arab community in Kenya is made up of several sub-groups, such as the Hadhrami Arabs, who came from Yemen, and the Omani Arabs, who came from Oman.
Another group of Semites in Kenya is the Jews.
Unlike the Arabs, the Jewish community in Kenya is small but vibrant, with a history that goes back over 100 years.
Most of the Jews in Kenya today are of Sephardic origin, with some also being Ashkenazi.
The Origin of Semites in Kenya
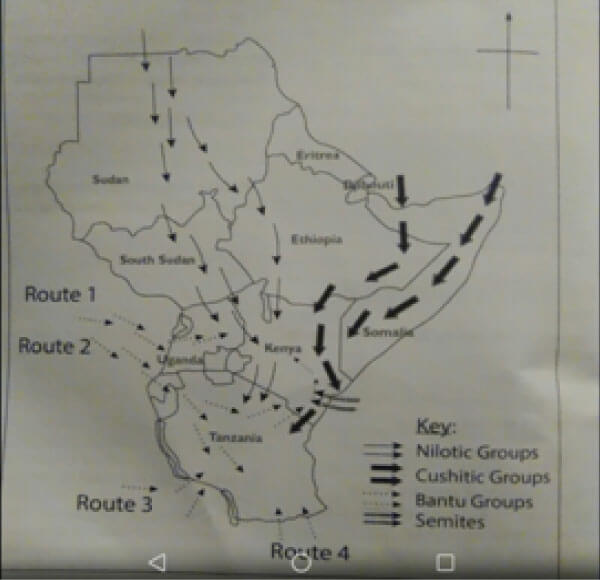
The origin of the Semites is believed to be in the middle east, precisely in present today Palestine, Syria, and Iraq.
From here, the Semites moved to other parts of the world including Kenya.
Some of the Semites migrated in search of trade opportunities and more favorable climatic conditions.
However, the biggest contribution to their migration was antisemitism which historians trace to as far back as 1096 AD.
Arabs were the first Semites to arrive in Kenya. They arrived at the coast of Kenya in 700 AD.
These Arabs were running away from the anti-Shia Ummayad dynasty and experts believe these Arabs were the ones that introduced Islam into the country.
Years later, the Yemeni Arabs also arrived at the coast from the Southern Arabia region.
Unlike the first batch that was running from persecution, the Yemenis had come to East Africa to explore trade opportunities with locals.
Even though they first settled at the coast, they eventually made inroads into the rest of the country and have consequently established communities that had a significant impact on the local culture.
Semitic Languages List
Semitic languages are a group of languages that are part of the Afro-Asiatic language family.
These languages include Tigrinya, Hebrew, Amharic, and Arabic.
Arabic is the most widely spoken Semitic language, with over 400 million speakers worldwide.
It is also an official language in many countries, including Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Morocco.
In fact, Arabic is so popular that it is the 5th most spoken language in the world (after Mandarin, Spanish, English, and Hindi).
The other Semitic languages are not as popular and are largely confined to their countries of origin e.g. Hebrew is mainly spoken in Israel although the Bible and the Christian faith may have made it more popular.
Impact of Semites in Kenya

The Semitic people have had a significant impact on Kenya’s culture, language, and religion.
Language
One of the most significant impacts has been on the Swahili language, which has a significant Arabic influence, with over 35% of its vocabulary derived from Arabic words.
This influence is due to the centuries-long contact between the Swahili people and Arab traders and settlers.
Historians believe that Swahili was formed when the Semites (mostly Arabs) intermarried with the Bantus in the coastal region.
Religion
The Semitic people have also had an impact on Kenya’s religion, with the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, all having their roots in the Middle East.
The Swahili coast, in particular, has a long history of Islamic influence, with some of the oldest mosques in the country located in Mombasa and Lamu.
Food
The cuisine of Semites has also left an indelible mark on Kenyan foods, especially along the coast.
Some of the foods that are now considered Kenyan were actually brought to the country by the Arabs.
Examples of such delicacies include biryani, pilau, and samosas.
The Semites also brought most of the spices that are commonly used in food preparation to date.
Arguably, the culinary culture of Kenya would be so boring without the influence of the Semites.
Architecture
Arabs have also impacted Kenyan architecture.
If you go to the coast, you will see lots of houses that have utilized the coral stones for construction.
Other influences include intricate wood carvings, Arabic calligraphy, and a “flat-roof” with a roof-top access design of houses.
Entertainment
There are some other less obvious influences that are worth noting.
For instance, Arab entertainment was imported into the country and today, Taarab music is almost a signature genre for the Swahili people.
Even the traditional dances like mazele and chakacha now have some elements of the Arabic dance and music style.
Trade
But perhaps the most important and often overlooked influence is trade.
Arab traders were among the first to establish trade links with East Africa, and their influence can still be seen in the types of goods traded and the way trade is conducted.
The use of bartering and haggling is still common in many parts of Kenya, particularly in traditional markets.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the history of Semites in Kenya is complex and fascinating.
They have had a significant influence on the country’s culture, language, and religion, and their impact can still be seen today.
Understanding the origins of Semites in Kenya is essential to appreciate the rich cultural heritage of the country.
For instance, Swahili is considered the national language of Kenya and this language wouldn’t even exist if the Semites had not settled in the country many years ago.
This serves to show what a huge impact the Semitic people have had on Kenya.

